Financial Reporting is the process of recording and presenting a company’s financial data in a clear and organized manner. In financial reporting, the average revenue, income, debts, and records are shown as liabilities. Through these reports, you can provide transparent information for the management, investors, and realtors, which helps in evaluating the overall financial health and future financial performance. Through financial reporting, you can gain a deeper understanding of your business’s overall financial performance and its regulatory adherence to SOC 2 and GDPR. This greatly helps the business to make accurate financial decisions and maintain transparency.
Introduction
If you own a business, you must have questioned yourself, “Where is the money going?” In a business, growth is measured by the countable figures. This is where the importance of financial reporting lies. Financial reporting plays a vital role in helping your business stay on track to reach its goals, and it also helps in future decision-making.
Atidiv is your trusted outsourcing partner who helps you build reports such as financial statements, budgeting, performance vs actuals, a daily/weekly KPI tracker to support decision making for actionable insights, and manage MIS
This blog is your ultimate guide for understanding what financial reporting is and the key aspects of financial reporting, its advantages, underlying risks, and effective measures to implement it. Let’s understand financial reporting in the simplest way possible.
What is Financial Reporting: Definition and Key Components
Financial reporting is the process of communicating a business’s financial activities over a specified period. Business uses this information to indicate the financial health. Financial reports play a crucial role in forecasting future profitability, assessing industry standing, and determining growth potential. Additionally, numerous financial reports are accessible for public examination.
So, what do you mean by the “Core” or “Key Components” of the financial reporting? Before knowing this, we must understand “What is a financial report?” Financial reports can be of any format that carries detailed information on the financial metrics, such as revenues, expenses, profits, capital, cash flow, and others are essential for monitoring historical performance, pinpointing critical areas for enhancement, and developing projections for possible future performance. These are the core of the financial reporting.
Now, let us take a deeper look at these key components: Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Cash Flow Statement.
1. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet gives a picture-perfect view of the business’s financial data. It records the total assets, liabilities, and equity. So what does the balance sheet hold? It has the elements that assist in the accounting equation. Balance sheets also provide a real-time assessment of your current asset liquidity and debt coverage. Balance sheets also provide a real-time assessment of your current asset liquidity and debt coverage.
| Assets = Liabilities + Equity |
Total assets would be the sum of the liabilities and equity. We will take a quick example. A balance sheet of a business for the latest accounting period or year
- Total assets: $200 billion
- Total Liabilities: $140 billion
- Total equity: $60 billion
Here, while calculating, we conclude that liabilities + equity($140+$60) equals the total assets($200) reported by the business.
2. Income Statement
The income statement, in simple terms, is the profit and loss statement. The income statement gives a detailed insight into the business’s overall revenue, expenses, profit, and loss over a particular period of time. Through this, you can analyse the business’s financial health. Each business has a unique method for calculating its income statements; some calculate it annually, while others maintain a quarterly record to monitor overall performance throughout the year.
A balance sheet is about analyzing the financial data of a fixed time period, for instance, ( Nov 20, 2025), while the income statement is the record for the whole accounting year. The basic structure of the income statement is
| Net Income= (Revenue+ Gains)- (Expenses+ Loss) |
We can understand the income statement with a simple example.
| Sales | $35,000 | |
| Revenue | Revenue | $5,000 |
| Total Revenue | $40,000 | |
| Procurement Costs | $12,000 | |
| Wages | $750 | |
| Rent | $2500 | |
| Expenses | Interest Paid | $500 |
| Transportaion | $300 | |
| Utilities | $150 | |
| Total Expenses | $16,200 | |
| Gains | Income from the sale of a thing | $2000 |
| Losses | Consumer lawsuit | $1000 |
| Net Income | (Revenue+ Gains)- (Expenses+ Loss) | $42,000- $17200= $24,800 |
This example is for a single-step income statement. Likewise, you can also calculate it by a multi-step income statement.
3. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement, or the statements of cash flows, gives an outline of how much cash the business generates over a period of time. Through this, you will get a clear picture of the liquidity and solvency. The cash flow statement can be calculated using operational activities, investing activities, and financing activities. A cash flow statement additionally assists lenders and investors in assessing the likelihood of repayment.
4. Statements of Changes in Equity
The statements of changes in equity are the reconciliation between the opening and closing balances of the shareholders’ equity. External stakeholders acquire insights into a company’s capital structure and the equity held by owners in financing the enterprise. Internal stakeholders mainly depend on this statement when determining whether to raise funds from owners or distribute dividends. The title of this statement varies according to the ownership configuration of the business: shareholder equity, partner equity, or owner equity.
What are the Top 5 benefits of Financial Reporting?
- Enhanced Decision Making: With the clear financial data, the team can arrive at better decisions. When decision-makers have access to transparent financial data, they can respond more swiftly to both risks and opportunities, whether it involves optimizing working capital or making investments for growth.
- Improved Transparency and Trust: Providing a clear and transparent view of the financial data will enhance trust. Creditors usually rely on these data to calculate the company or business’s ability to repay the debts. These transparent financial data will help the employees to understand the financial stability of the business.
“Transparency in Financial Reporting is critical for fostering trust and confidence among the investors and stakeholders- John A Tracy.”
Compliance with Regulations:
- SOC 2 is the Service Organization Control that has security over sensitive data. It guarantees that outsourced accounting firms uphold strong internal controls and protect client information from unauthorized access or misuse.
- GDPR adherence means that the outsourced accounting firm is compliant with the General Data Protection Regulation of the European Union, ensuring that the personal and financial data are protected. It makes sure your business information is treated with security, transparency, and in full accordance with international privacy standards.
- Benchmarking: The financial report helps the business to compare the financial metrics with those competitors. Through this, businesses can understand their strength and weaknesses.
- Better Performance Evaluation: The regular analysis of the financial reports assists companies in evaluating their performance relative to established goals, objectives, and industry standards. This allows management to pinpoint strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to tackle any challenges and seize growth opportunities.
Underlying Risks of Poor Financial Reporting
- Reputational damage: Do you know what is the backbone of any business? It is the trust. Any financial inaccuracies or misinterpretation of data can severely damage the overall reputation of the business. This can lead to a lasting impact on the business.
- Compliance Failures: As a business owner, are you familiar with the factors that cause compliance failures? Compliance failure occurs when the business fails to follow the industry standards, guidelines, and required laws for recording the financial information. The businesses need to focus on these factors. Failure to follow these standard regulations to lead to legal consequences, loss of trust, and poor decision-making.
- Operational Disruptions: We know that correcting the financial records is time-consuming and tiring. This can significantly affect the business hours, impacting the overall performance and loss of resources.
- Potential for Fraud: Intentional manipulation of the financial records can lead to serious financial and reputational damage to the business.
What are the Use Cases of Financial Reporting?
Wondering what “Use Cases of Financial Reporting” means? The financial reporting is used by both the internal and external stakeholders for different reasons. It can be considered as a different situation, or a purpose for which the financial report is prepared to or used for getting into important conclusions, or making a decision, or to solve an existing business problem, or to support a business operation. With the “Use Cases” of financial reporting, the business can track the overall performance, plan the budget, and have a record of the overall financial health of the business. Take a look at some of the important use cases of financial reporting.
1. Internal Management Analysis
So, what is internal management analysis? The financial reporting is being used by the internal management to have a detailed understanding of the financial operations and take the right decisions i the future to reduce the internal cash flows. These are not just a final report; they include KPI dashboards, budget, reports, and the overall analysis of the cash flow.
2. Investor Relations
Financial reporting enables companies to convey their performance, stability, and growth potential to investors, shareholders, banks, and lenders. At the conclusion of each quarter, publicly traded companies submit a Form 10-Q to the SEC, which serves as a crucial financial report for investors and the public markets. The 10-Q contains unaudited financial statements along with summary commentary from the company’s management, in addition to supplementary disclosures and schedules pertaining to the recently concluded quarter and the fiscal year thus far. In many respects, it resembles a “mini” annual 10-K. These financial reports are significant as they offer the public three periodic updates throughout the year regarding a company’s performance, eliminating the need to wait for 12 months for an annual 10-K.
3. Regulatory Compliance
In the US, all companies must follow the standard accounting rules and other requirements. Regulators are implementing strict standards for corporate information to enhance their supervision of the companies within their jurisdiction, encourage transparency, and protect the interests of various stakeholders. Financial reporting analytics powered by XBRL data can enhance companies’ adherence to regulations by providing insights that assist them in delivering thorough reports that address all inquiries. The business ensures that the financial reporting complies with the GAAP, IRS tax reporting, SEC guidelines, and industry regulations.
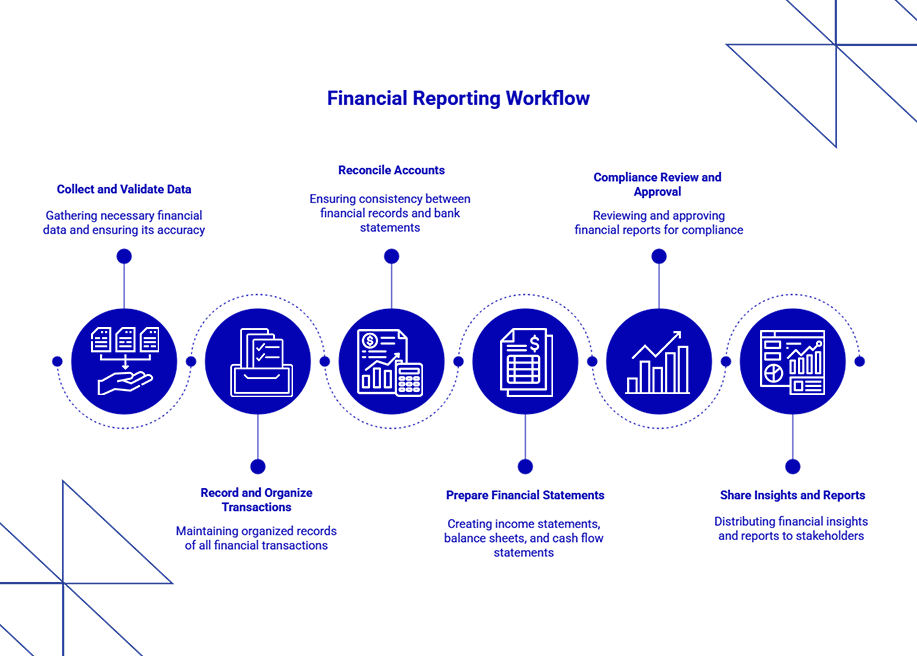
Let us take a closer look at the implementation steps of Financial Reporting
Now, you have a clear understanding of “What is financial reporting?”, we will take a closer look at the implementation steps. The implementation step is a structured procedure that you need to follow to create an accurate financial report. Here is the step-by-step guide for you to follow the implementation steps of financial reporting.
1. Identify Reporting Requirements
Before creating a financial report, the business needs to have a clear understanding of who should receive this report. Whether the report is prepared for internal planning, regulatory purposes, or investor updates. Identifying the purpose of creating the report will give you a clear idea of determining the format, level of detail, and key metrics to be included.
2. Gather all financial data
The next step is to get all the relevant data, which is the key ingredient of the financial reporting. This data includes sales, assets, and liabilities that can be collected from the general ledger, CRM, or other integrated system. 64% of the businesses say that their decisions are mostly data-driven.
3. Create Financial Statements
What comes in this step? This is where the financial statements actually take their final form. The report is created where you include the “core elements” like Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Cash Flow Statement. Always ensure that you are maintaining accuracy.
4. Run a review and accuracy check
As a business owner, you must know how important it is to double-check the data before finalizing or presenting it. Have a detailed review with the key stakeholders and other partners to validate your assumptions, check for errors, whether you have added all the numbers and that everything is in line with the industrial standards.
5. Share safely and Store for Compliance
This is the final and most important step. The final report is shared with the regulatory authorities or whoever needs it. The report is saved in a safe and accessible format, like a PDF or a documentation link. If you are sharing it externally, ensure to maintain version control and frequent audit trails.
Understanding Tooling and Workflows in Financial Reporting
Financial Reporting is not just about collecting numbers and preparing a report; it is all about using effective tools and ensuring the smooth workflow of the financial data. By using these tools, the business can improve the financial statement accuracy. The major advantages of using these tools are that you can minimize the manual tasks, fewer errors, optimize workflows, improve collaboration among process stakeholders, and adhere to regulatory requirements. These are some of the recommended tools for financial reporting.
- For small businesses, use accounting software tools like QuickBooks, Zero, and Wave
- An ERP system like Oracle NetSuite, Sage, SAP, and so on is used for large businesses and enterprises.
- For special needs, you can use software tools like Microsoft Excel, Sage, Google Looker Studio, and so on.
Related| Bookkeeping Software tools every business should know
What are the Key risk areas of financial reporting?
Though the financial reporting has many benefits, it also has some pitfalls that need to be paid attention to. These are some of the major risk areas of financial reporting.
- Inaccurate Data Entry: One of the major pitfalls of financial reporting is entering inaccurate data. This usually occurs during the manual data entry process.
- Lack of clarity on compliance awareness: There are no stable financial rules. It keeps on changing. The business needs to stay updated to avoid penalties, non-compliant reporting, and misinterpretations of new standards.
- Missing insights from stakeholders: While preparing the financial reports, it is important to collect crucial information from the key stakeholders. This can lead to inaccurate assumptions and records.
- Inconsistent Accounting Practices: When you are following a rule and the team applies a completely different format of reporting, then there will be a mishap.
- Missed Deadlines: Financial reporting is sensitive data that needs to be updated within the deadline. Any delay or rushed compilation can lead to errors.
Compliance Considerations of Financial Reporting
More than just numbers, financial reporting is all about adhering to the standard industry standards and maintaining transparent records, and also conducting regular audits. These are the industry standards that need to be taken into account.
- SOC 2 guarantees that the system is secure from unauthorized access. It also ensures that all the sensitive and confidential data is secured.
- GDPR adherence means that the outsourced accounting firm is compliant with the General Data Protection Regulation of the European Union, ensuring that the personal and financial data are protected. It makes sure your business information is treated with security, transparency, and in full accordance with international privacy standards.
- HIPAA is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. It sets the security standards for the protection of PHI. HIPAA in financial reporting is important as it sets standards for protecting the sensitive data of the patient. HIPAA compliance builds trust wth the patient. It reduces the compliance errors and thus improves the operational efficiency.
What are the practical checklists for Financial Reporting?
Take note of the practical checklist for financial reporting for the year 2026.
- Set a definite reporting objective: With clear objectives, you can have the clarity of what should be included in the financial report.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Double-checking is the key. Ensure that all the data entered is correct, up to date, and error-free.
- Validate Compliance Requirements: It is very important to make sure that the financial reports your business has are in adherence with the industry standards (GDPR, SOC 2, HIPAA) are specific to industry regulations.
- Maintain a regular reporting interval: Maintain a consistent reporting interval- weekly, monthly, quarterly, and annually. This is to avoid the last-minute rush.
Final thoughts
Financial reporting is an important process for understanding your business better. With the regular review of your balance sheet, cash flow statements, and income statements, you can keep track of your business’s financial health and plan the future accordingly. With accurate financial reporting, you can reduce the risks, maintain organized data, which will enhance the credibility of your business with the key stakeholders. This blog must have given you a clear insight into “What is financial reporting?”, benefits, pitfalls, compliance, and many more. With proper planning, you can enhance the overall financial health of your business.
Are you ready to make your financial reporting simpler and more effective? Atidiv is your trusted outsourcing partner for getting tailored solutions for your business needs. Contact us today!
Frequently Asked Questions on Financial Reporting
1. What happens if my financial data is not correct?
The incorrect financial data can often lead to misguided decisions that can affect the overall performance and profitability of your business. This can gradually cause penalties and reputational damage.
2. What is the estimated time for implementing the financial reporting?
Financial reporting often varies from a few weeks to several months. It mainly depends on the complexity of the task, data, and the compliance to be adhered to.
3. Name some of the best tools for financial reporting?
Some of the best tools for financial reporting are QuickBooks, NetSuite, Xero, Wave Accounting, Sage, FreshBooks, and so on.
4. How can I make sure that my business complies with the Industry regulations?
In order to make sure that your business complies with the industry standards, it is important to conduct regular audits, stay updated with the regulations, and make use of advanced technologies.
5. Is it possible to outsource the financial Reporting in 2026?
Yes, it is possible for the business to outsource financial reporting with a trusted partner. Atidiv has years of experience in outsourcing finance and accounting for major businesses.
6. What is the average cost for financial reporting as per the US markets’ standards?
There is no specific estimation. It can usually vary depending on the process, complexity, and the task performed. For small businesses, the average cost can usually vary between $1000 and $5000 per year.
7. How can I manage if my team is lacking strong financial expertise?
Any business must have a great financial team to maintain the crucial financial data with utmost accuracy. You can seek external support or advice in this scenario. You can also outsource finance and accounting services.
